COST Hata model
The COST-Hata-Model is the most often cited of the COST 231 models. Also called the Hata Model PCS Extension, it is a radio propagation model that extends the Hata Model (which in turn is based on the Okumura Model) to cover a more elaborated range of frequencies.[1] COST (COperation européenne dans le domaine de la recherche Scientifique et Technique) is a European Union Forum for cooperative scientific research which has developed this model accordingly to various experiments and researches.
Contents |
Applicable To / Under Conditions
This model is applicable to urban areas. To further evaluate Path Loss in Suburban or Rural Quasi-open/Open Areas, this path loss has to be substituted into Urban to Rural/Urban to Suburban Conversions. (Ray GAO, 09 Sep 2007)
Coverage
- Frequency: 1500 MHz to 2000 MHz
- Mobile Station Antenna Height: 1 up to 10m
- Base station Antenna Height: 30m to 200m
- Link Distance: 1 up to 20 km
Mathematical Formulation
The COST-Hata-Model is formulated as,
![L \; = \; 46.3 \; %2B \; 33.9\log f \; - \; 13.82 \log h_B \; - \; a(h_R) \; %2B \; [44.9 \;- \;6.55 \log h_B] \log d \; %2B \; C](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/20edab396b0bc2bf532d2a456a5fade8.png)
For suburban or rural enviorenmments:
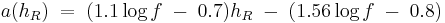

Where,
L = Median path loss. Unit: Decibel (dB)
f = Frequency of Transmission. Unit: Megahertz (MHz)
hB = Base Station Antenna effective height. Unit: Meter (m)
d = Link distance. Unit: Kilometer (km)
hR = Mobile Station Antenna effective height. Unit: Meter (m)
a(hR) = Mobile station Antenna height correction factor as described in the Hata Model for Urban Areas.
Points to Note
The European Co-operative for Scientific and Technical research (EUROCOST) formed the COST-231 working committee to develop an extended version of the Hata model. COST-231 proposed the following formula to extend Hata's model to 2 GHz. The proposed model for path loss is
L50(urban) = 46.3 + 33.9 log fc - 13.82 log hte - a (hre) + (44.9 - 6.55 log hte) log d + Cm where a(hre) is the correction factor for effective mobile antenna height which is a function of the size of the coverage area.
0dB for medium sized city and suburban areas
Cm =
3 dB for metropolitan centers
The COST-231 extension of the Hata model is restricted to the following
range of parameters:
f : 1500 MHz to 2000 MHz hte :3Omto200m hre :lmtolOm d :lkmto2okm
Limitations
This model requires that the base station antenna is higher than all adjacent rooftops.
References
- ^ Final report for COST Action 231, Chapter 4